
"Sudden" outbreaks of diseases of microbial origin in valuable aquatic farmed species (fish and crustacea) cause significant economic consequences for the aquaculture industry worldwide, due to increased mortality and reduced performance. Furthermore, medical treatments of sick animals raise scepticism of consumers about aquaculture’s quality and credibility.
One of the most devastating bacterial diseases for aquaculture is called vibriosis. This disease can be caused by over 20 species of the gram-negative Vibrio bacteria., such as V. vulnificus or V. parahaemolyticus. These microorganisms also have zoonotic potential and can become a serious threat for human health, as they accumulate in the reared animal’s flesh.
Antibiotic treatments to reduce the negative impacts of vibriosis can lead to undesirable side effects, such as toxicity to the reared animals, and increase the environmental impact. Furthermore, it was reported that some pathogenic Vibrio strains are resistant to several antibiotics. This raises the growing need for new effective prophylactic methods to reduce the use of antibiotics with their undesirable side effects in modern aquaculture.
Fertility problems are often caused by chronic endometritis (inflammation of the inner uterine epithelium) and impaired ovarian function. Even though the general state of affected cows is apparently healthy, the inflamed uterus affects the fertilization of the oocyte, or, if conception is successful, it can lead to abortions due to an unfavorable uterine environment. Furthermore, it has been reported that inflammation of the uterus can negatively impact ovarian function. Dystocia (prolonged, difficult birth), retained placenta and clinical metritis (uterine inflammation) are common risk factors that can lead to the development of chronic subclinical endometritis. Though hygienic conditions during parturition and proper assistance of the dam during, and immediately after calving are critical for the prevention of metritis, cow management throughout the dry and transition periods is also critical. Excessive body condition at calving, a profound and prolonged negative energy balance that could lead to ketosis, and hypocalcemia are risk factors for dystocia, retention of fetal membranes and clinical metritis which could eventually lead to chronic subclinical endometritis.
Vibriosis in fish usually starts with dermal ulceration, which, if untreated, is followed by systemic infections and septicaemia. The infection manifests in lethargy, anorexia, abnormal swimming, ulcerative and haemorrhagic skin lesions, abdominal distension, exophthalmia or “pop-eye”, gill necrosis, darkened skin, and death.
In shrimp, systemic vibriosis typically results in lesions of the cuticle, cloudy muscle tissue, formation of septic nodules in the lymphoid organ, heart, gills, hepatopancreas, antennal gland, nerve cord, telson and muscle, brown or black lesions on the cuticle, appendages or gills, and tail necrosis. Affected postlarvae may often display brown gills, cloudy and/or septic hepatopancreata – characterised by atrophy of the hepatopancreas with multifocal necrosis and haemocytic inflammation, loss of the epithelium of the midgut, and many more.
Since Vibrio spp. need adherence and multiplication in the host, a combination of the following control and preventive measures should be implemented to prevent the disease development:
Кроме того, полезно укреплять целостность кишечника и защитные системы организма с помощью пребиотиков/пробиотиков и кормовых добавок, стабилизирующих здоровье кишечника, таких как фитогенные кормовые добавки, например Sangrovit. Эти добавки не только способствуют росту, снижают стресс и уменьшают количество вибрионов, но и безопасны для животных, человека и окружающей среды. Научное исследование, проведенное в Университете Касетсарт, продемонстрировало следующие положительные эффекты Sangrovit на нильскую тилапию (Oreochromis niloticus).
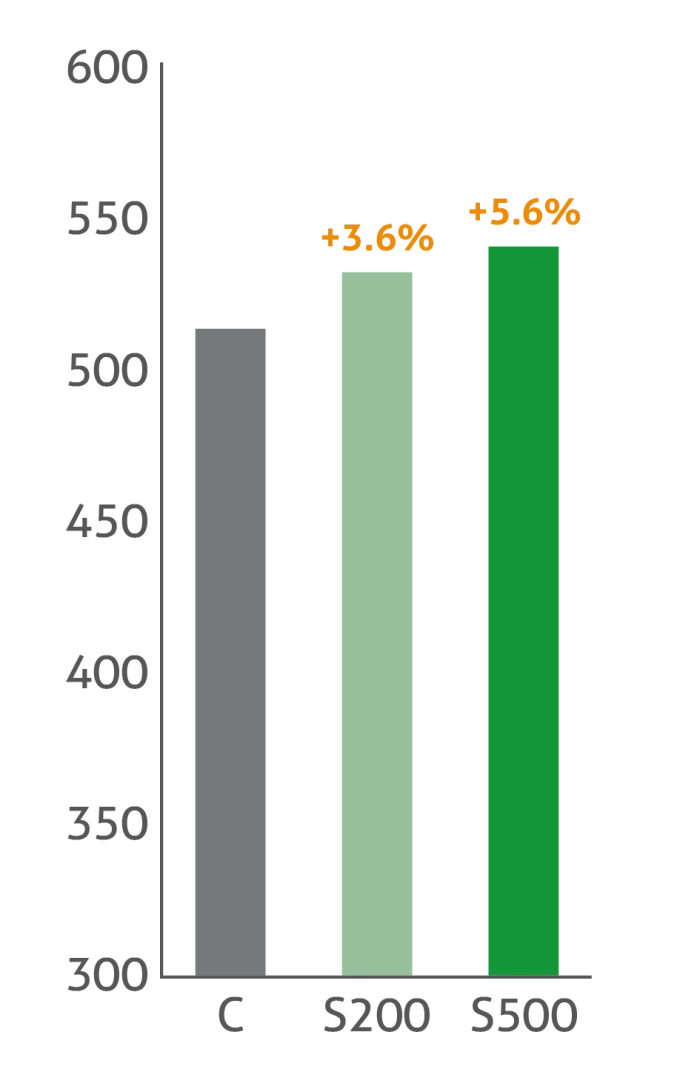
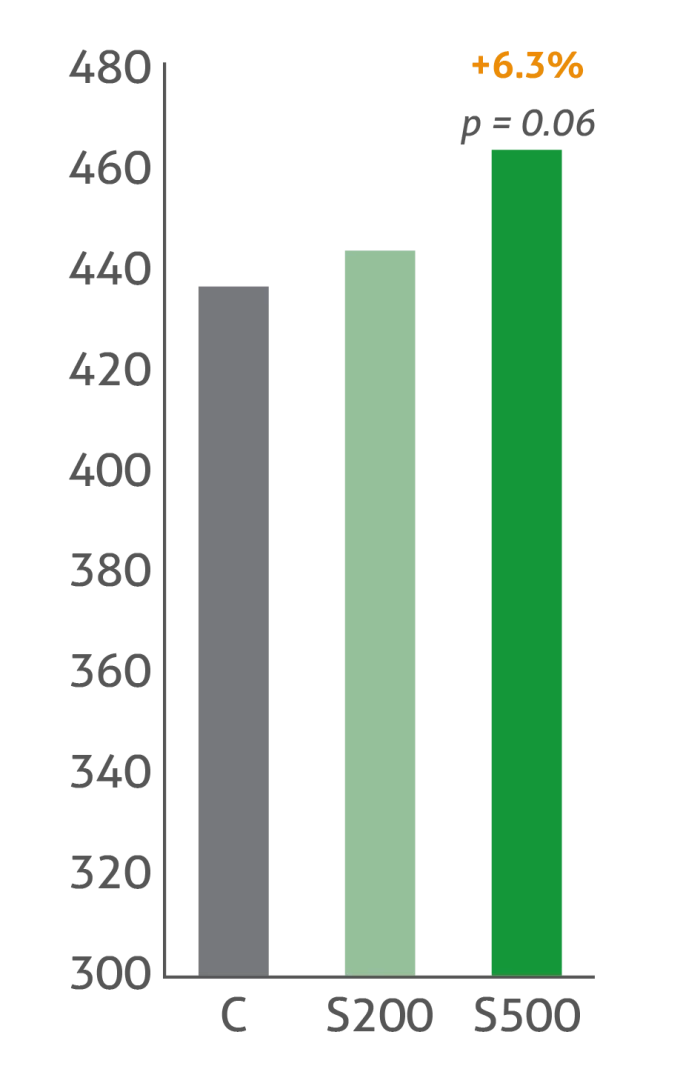
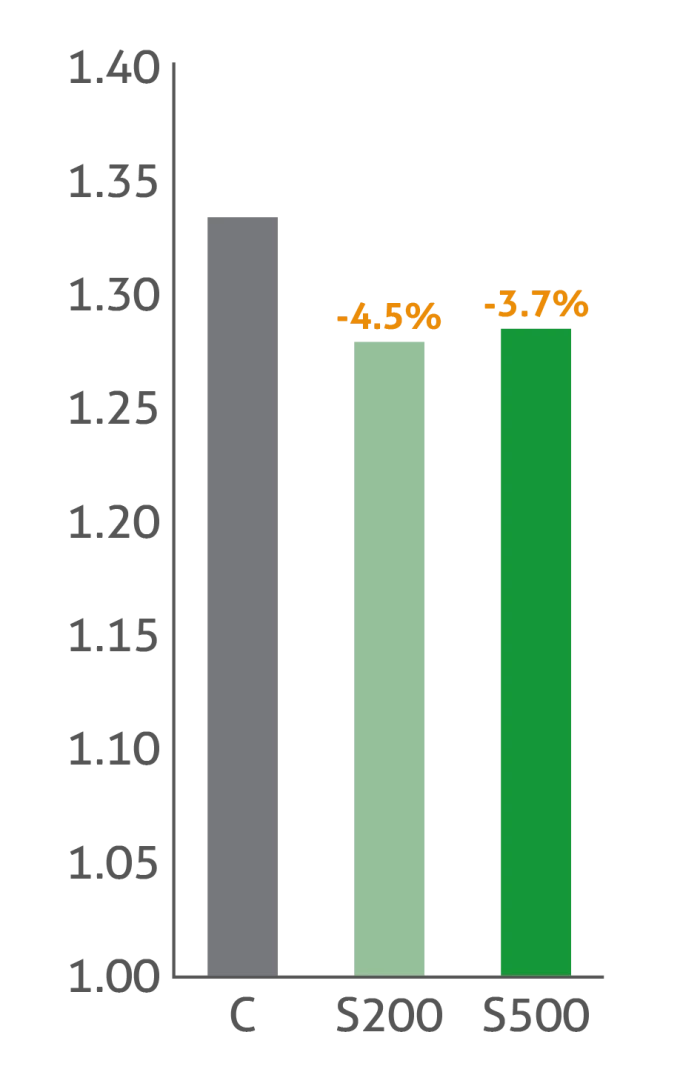
Increased body weight and feed intake while reduced FCR
Treatment groups: C: Control | S200: Sangrovit® 200 g/t | S500: Sangrovit® 500 g/t
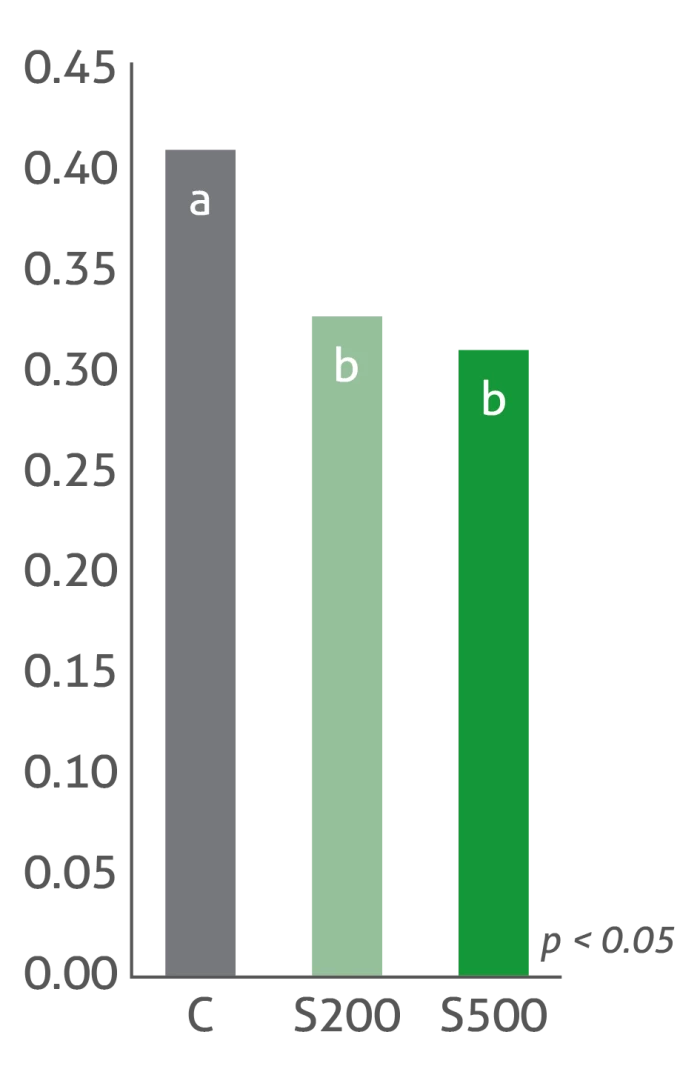
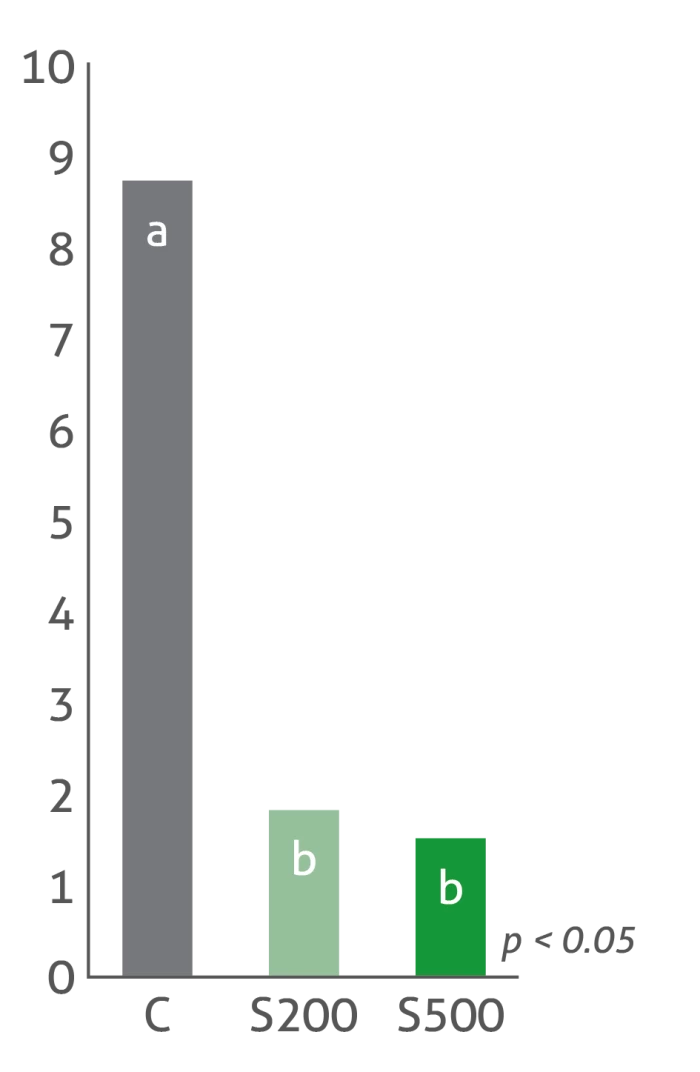
Strong decrease in stress hormone
Contact our experts or send us a message. We will contact you as soon as possible.